Covid Vaccine Pregnancy Pubmed
WHOs global commitment to fair access to COVID-19 vaccines should therefore include pregnant women. Do pregnant women wish to be vaccinated against COVID.
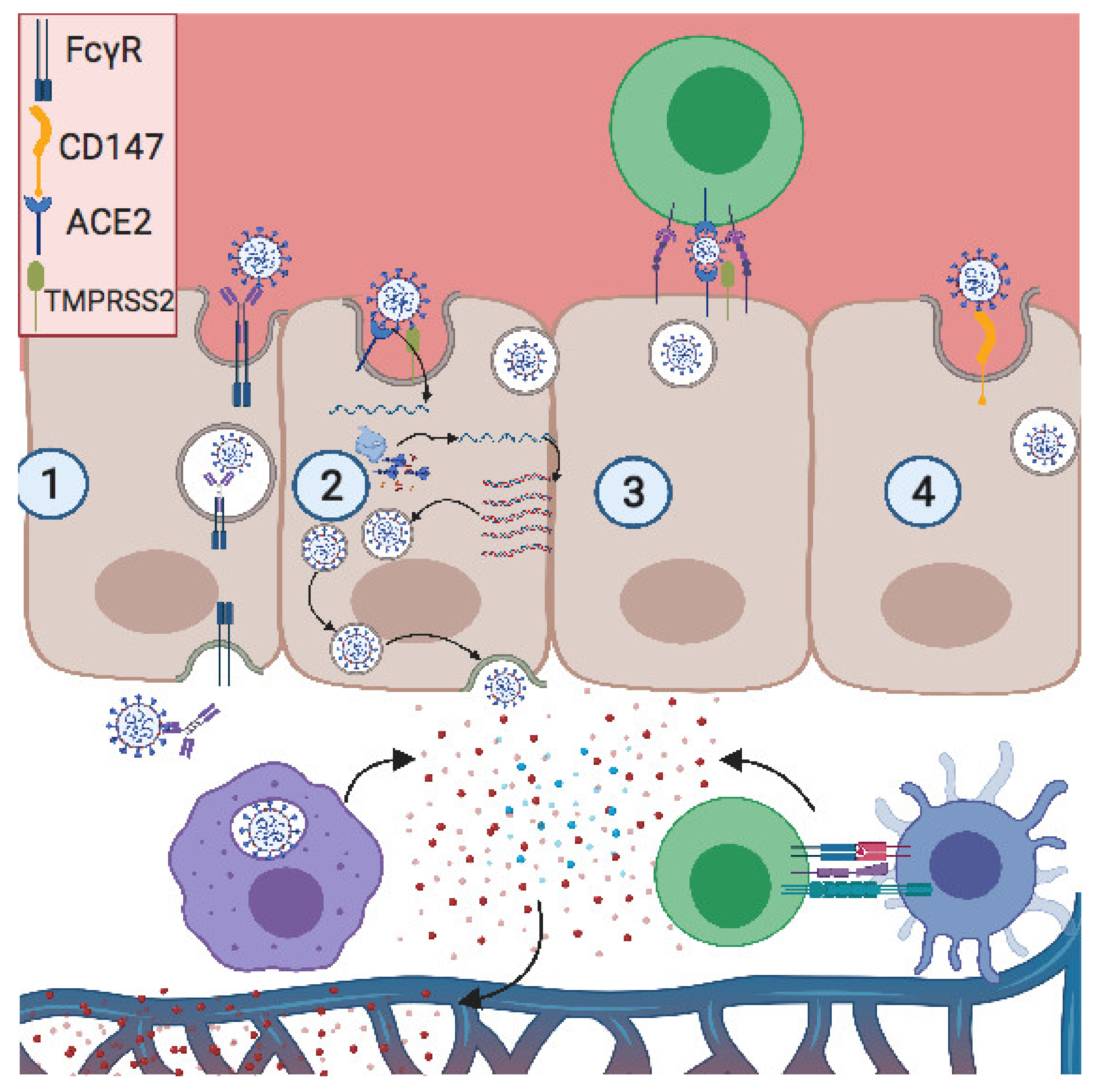
Vaccines Free Full Text Covid 19 And Pregnancy Vertical Transmission And Inflammation Impact On Newborns
Pregnancy Complications Infectious prevention control.

Covid vaccine pregnancy pubmed. In this study we estimated that the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine is as effective for pregnant women as previously reported for the general population during the same time period. In this exploratory analysis of a convenience sample receipt of a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine was immunogenic in pregnant women and vaccine-elicited antibodies were transported to infant cord blood and breast milk. Vaccines in pregnancy and the COVID-19 vaccine Decades of experience with other vaccines administered during pregnancy would suggest that we could expect a similar result for the COVID-19 vaccine in pregnant people compared to non-pregnant individuals.
In the United States by 10 February 2021 20000 pregnant people had received a COVID-19 vaccine and enhanced pharmacovigilance of these vaccine. Vaccine-induced antibody titers were equivalent in pregnant and lactating compared with nonpregnant women pregnant median 559. Because pregnant persons were excluded from the initial phase 3 clinical trials of COVID-19 vaccines limited data are available on their efficacy and safety during pregnancy.
The data so far suggest that it is and given the increased risks associated with COVID-19 in pregnancy many pregnant people have decided to accept the vaccine. Scopus 153 Google Scholar 2. Individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding can choose to receive authorized COVID-19 vaccines and studies to gather safety data in these populations are ongoing.
When pregnant people receive an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy their bodies build antibodies against COVID-19 similar to non-pregnant people. The shots didnt have final approval from the Food and. When COVID-19 vaccines became available to pregnant women in their states this spring both Harrison 36 and Nipper 29 decided to wait.
So far COVID-19 vaccines appear to be safe in these populations. Guidance regarding whether pregnant persons should receive a COVID-19 vaccine is needed. Antibodies made after a pregnant person received an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine were found in umbilical cord blood.
Vaccines in general are safe efficacious and produce an effective immune response when. After developmental and reproductive toxicology studies are completed some companies are expected to conduct clinical trials in pregnant persons. Over time real-world evidence from other countries has accumulated and reports show that.
29 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a health advisory recommending urgent action to increase COVID-19 vaccination among people who are pregnant trying to or might become pregnant or were pregnant recently in order to prevent serious illness death and adverse pregnancy outcomes due to the coronavirus infection. To enable the inclusion of pregnant and lactating women in the development of COVID-19 vaccines three key questions need to be answered. The recommendations for use of the COVID-19 Pfizer and Moderna vaccine in pregnant and lactating women now range from avoidance of the vaccineas recommended by the World Health Organization and some regulatory agenciesto reliance on recipients to make choices guided by their values or their clinicians judgement5 79 Some regulatory bodies recommend against pregnancy in the weeks following the vaccine.
4 The potential harms to pregnant. All titers were significantly higher than those induced by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection during pregnancy. Although not directly comparable the proportions of adverse pregnancy.
There is no evidence that COVID-19 vaccines have any effect on fertility or your chances of becoming pregnant. This means COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy might help protect babies against COVID. The rationale for the recommendations of vaccine avoidance in pregnancy.
In the meantime those who are planning pregnancies. Vaccination of pregnant people builds antibodies that might protect their baby. It is essential that we improve our knowledge of these vaccines and of their adverse drug reactions in this sensitive population of pregnant women which is why the French pharmacovigilance centres and the Agence nationale de sécurité du médicament et des produits de santé ANSM the French Drug Agency have set up a COVACPREG COvid VACcine PREGnancy cohort in May 2021.
The NIAID study will build on these studies by improving the understanding of antibody responses to COVID-19 vaccines among pregnant. When pregnant women wish to be vaccinated doctors must explain that long-term adverse reactions to COVID-19 vaccination have not been identified and that safety for fetuses and offspring has not been established. So is COVID-19 vaccination safe during pregnancy.
The initial advice from immunisation expert groups was therefore cautious and COVID-19 vaccines were not routinely recommended in pregnancy. Accordingly we advocate that pregnant women should be included in the phase 3 trial protocols of adenovirus-vectored vaccines and also protein-based vaccines. Spontaneous abortions did not have an increased odds of exposure to a COVID-19 vaccination in the prior 28 days compared with ongoing pregnancies adjusted odds ratio 102.
By monitoring the outcomes for these people and their babies we will soon be able to make evidence-based recommendations on whether the vaccines should be rolled out to pregnant people more widely. 4 5 Clinical trials demonstrate that vaccination is highly effective in preventing symptomatic COVID-19 in non-pregnant patients. Pregnant women are not ineligible for COVID-19 vaccination in light of the current spread of COVID-19 infection.
The aim of this study is to monitor potential adverse drug reactions of vaccination in pregnant. What is the short-term and long-term burden of COVID-19 in pregnant women the fetus and infants in all populations and ethnic groups. Solicited local and systemic reactions that were reported to the v-safe surveillance system were similar among persons who identified as pregnant and nonpregnant women.
A COVID-19 vaccine was received within 28 days prior to an index date among 80 of ongoing pregnancy periods vs 86 of spontaneous abortions. Time of initial guidance there was limited evidence confirming the safety of COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy. Interquartile range 477-598 P24.
Pregnant and nonpregnant women who were vaccinated developed cross-reactive antibody responses and T-cell responses against. There is no need to avoid getting pregnant after COVID-19 vaccination. The doctor should obtain consent and follow up the pregnant woman in the hospital for 30 minutes.
It is notable that as of April 26 2021 more than 100000 pregnant women reported having received a Covid-19 vaccination and yet only a small fraction 47 have enrolled in the v-safe pregnancy. Surveillance review of the safety of mRNA Covid-19 vaccines during pregnancy and the periconception period indicates that some pregnant persons in the United States are choosing to be vaccinated against Covid-19 in all trimesters of pregnancy. Although some live vaccinations such as measles mumps and rubella and varicella are contraindicated in pregnancy all current COVID-19 vaccines are composed of double-stranded DNA or mRNA and do not carry the live virus Table.
Pregnant women who are at increased risk of adverse outcomes from COVID-19 would be additionally harmed if they were unable to access evidence-based chemoprophylaxis from vaccine trials.

Immunity To Sars Cov 2 Induced By Infection Or Vaccination Castro Dopico Journal Of Internal Medicine Wiley Online Library
Looking Beyond Covid 19 Vaccine Phase 3 Trials Nature Medicine
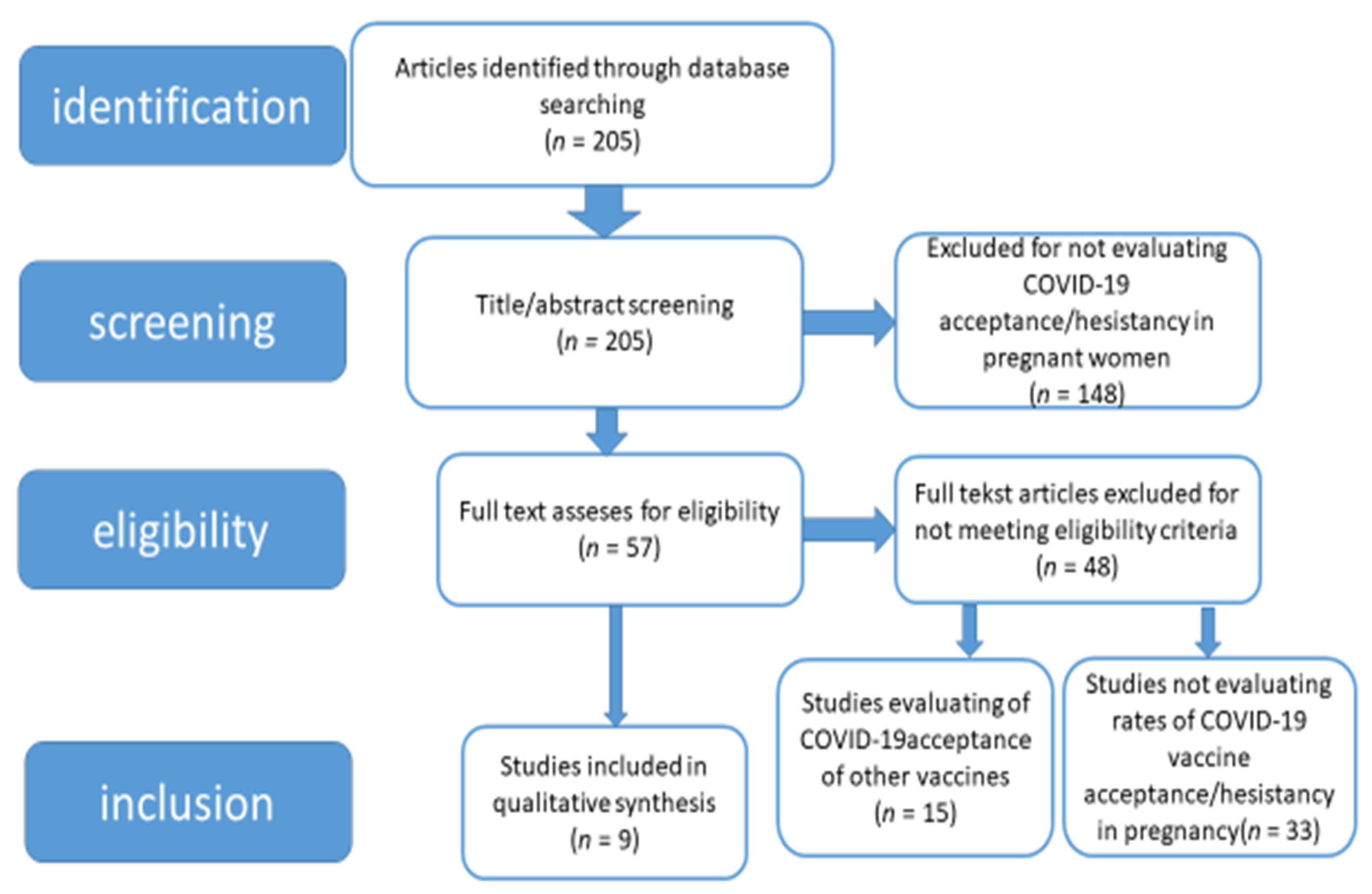
Medicina Free Full Text The Approach Of Pregnant Women To Vaccination Based On A Covid 19 Systematic Review Html
The Effect Of Coronavirus Infection Sars Cov 2 Mers Cov And Sars Cov During Pregnancy And The Possibility Of Vertical Maternal Fetal Transmission A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis European Journal Of Medical Research Full Text
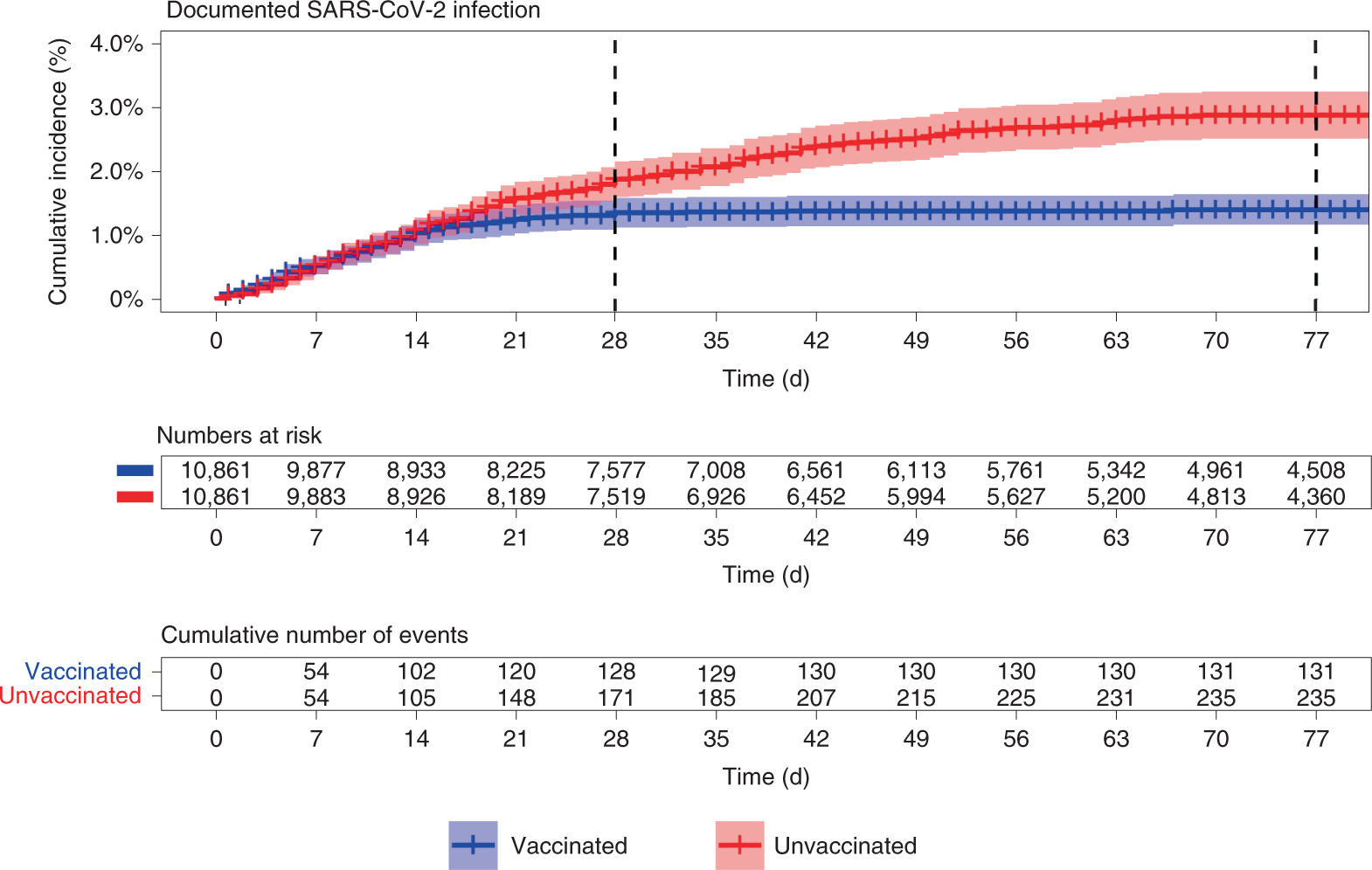
Effectiveness Of The Bnt162b2 Mrna Covid 19 Vaccine In Pregnancy Nature Medicine

An Interactive Website Tracking Covid 19 Vaccine Development The Lancet Global Health
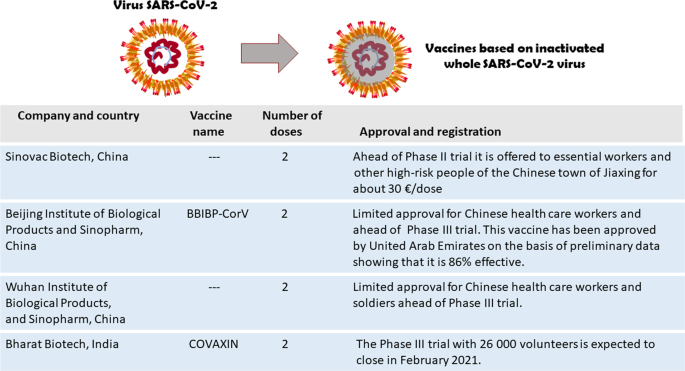
Covid 19 Vaccines Where We Stand And Challenges Ahead Cell Death Differentiation
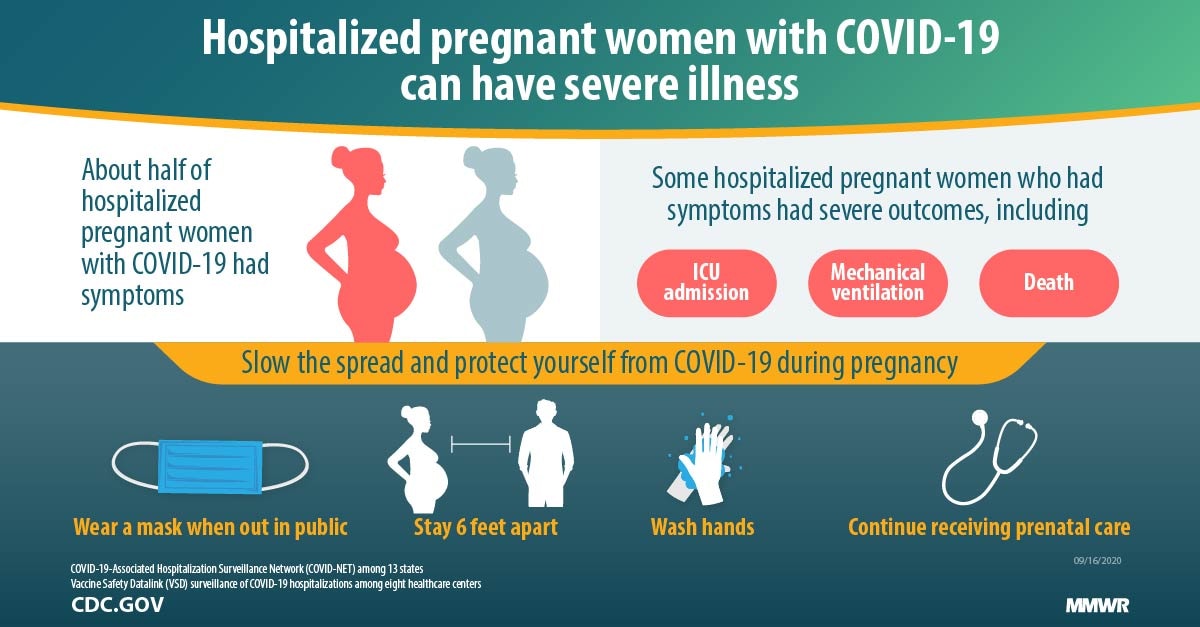
Characteristics And Maternal And Birth Outcomes Of Hospitalized Pregnant Women With Laboratory Confirmed Covid 19 Covid Net 13 States March 1 August 22 2020 Mmwr

Sars Cov 2 Vaccination For Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease A British Society Of Gastroenterology Inflammatory Bowel Disease Section And Ibd Clinical Research Group Position Statement The Lancet Gastroenterology Hepatology

Pregnancy And Covid 19 Physiological Reviews

Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccine Response In Pregnant And Lactating Women A Cohort Study American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology
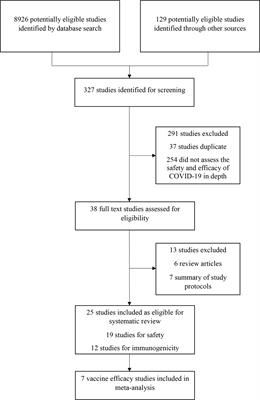
Frontiers Efficacy Immunogenicity And Safety Of Covid 19 Vaccines A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Immunology
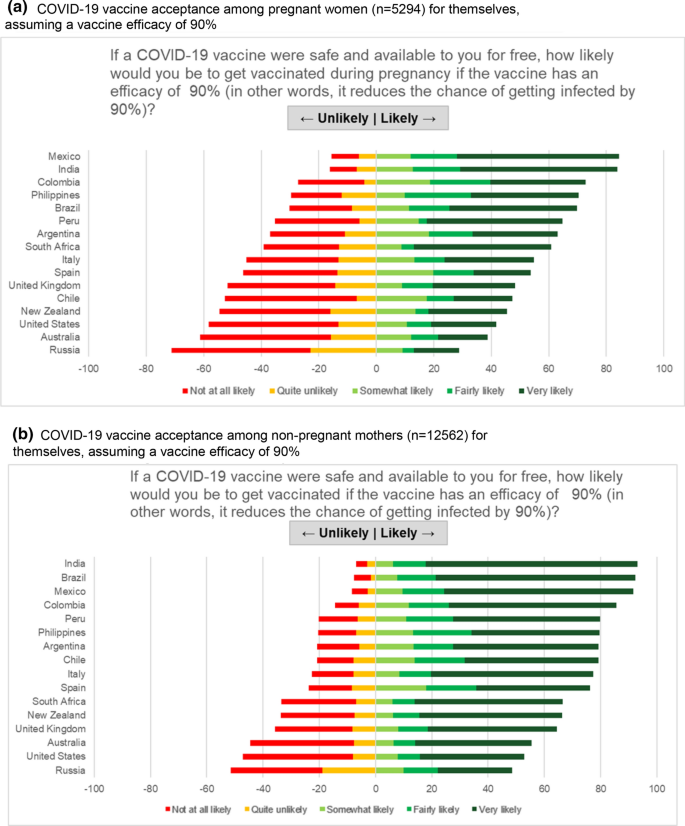
Covid 19 Vaccine Acceptance Among Pregnant Women And Mothers Of Young Children Results Of A Survey In 16 Countries Springerlink

Global Regional And National Estimates Of Target Population Sizes For Covid 19 Vaccination Descriptive Study The Bmj

Safety And Protective Effects Of Maternal Influenza Vaccination On Pregnancy And Birth Outcomes A Prospective Cohort Study Eclinicalmedicine
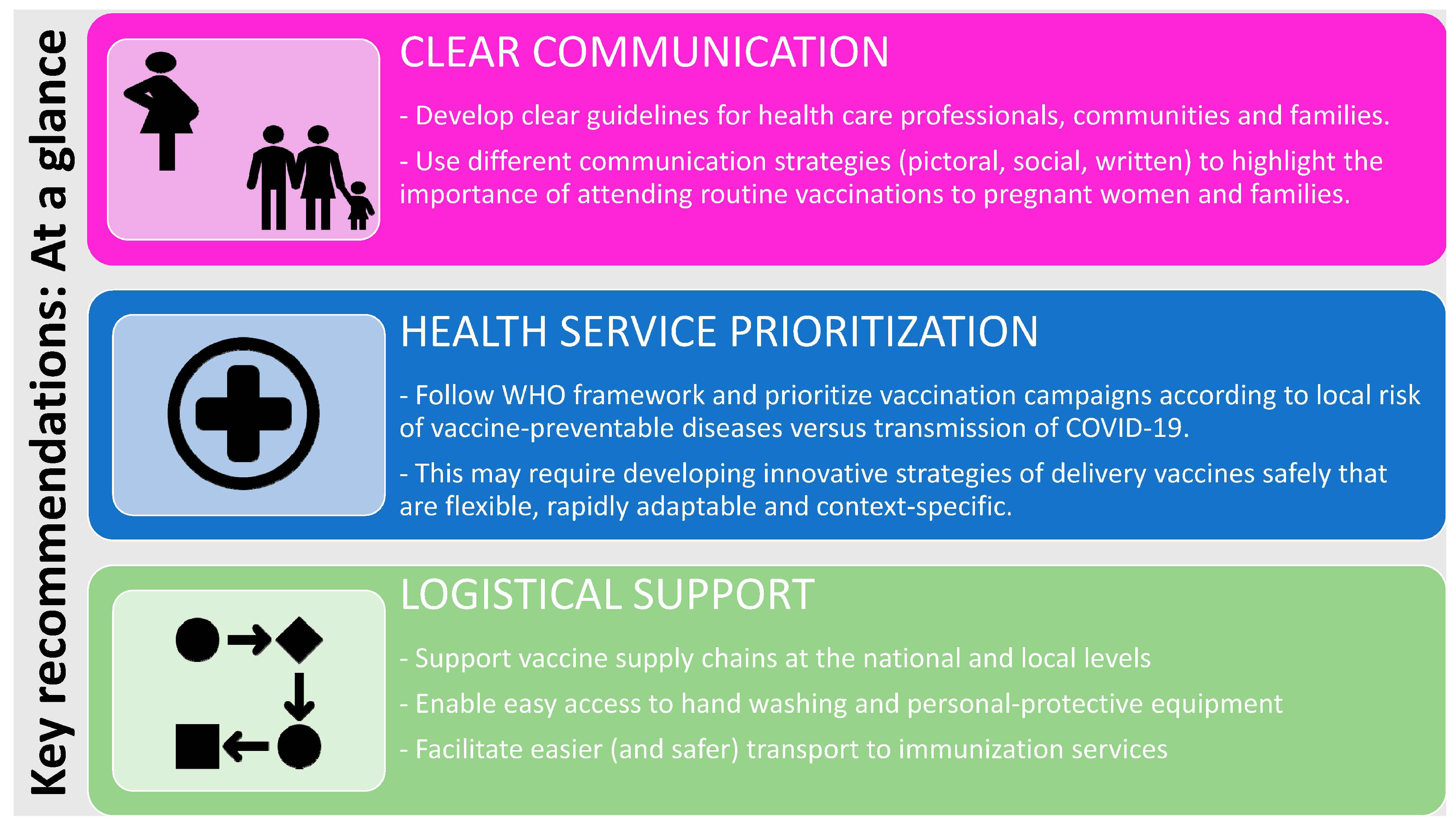
Vaccines Free Full Text Impact Of Covid 19 On Immunization Services For Maternal And Infant Vaccines Results Of A Survey Conducted By Imprint The Immunising Pregnant Women And Infants Network Html
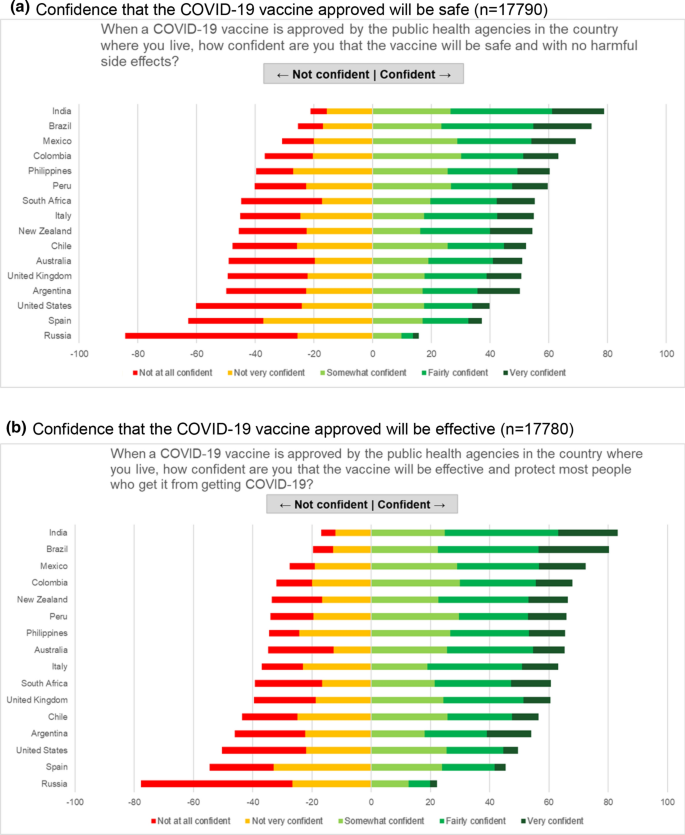
Covid 19 Vaccine Acceptance Among Pregnant Women And Mothers Of Young Children Results Of A Survey In 16 Countries Springerlink
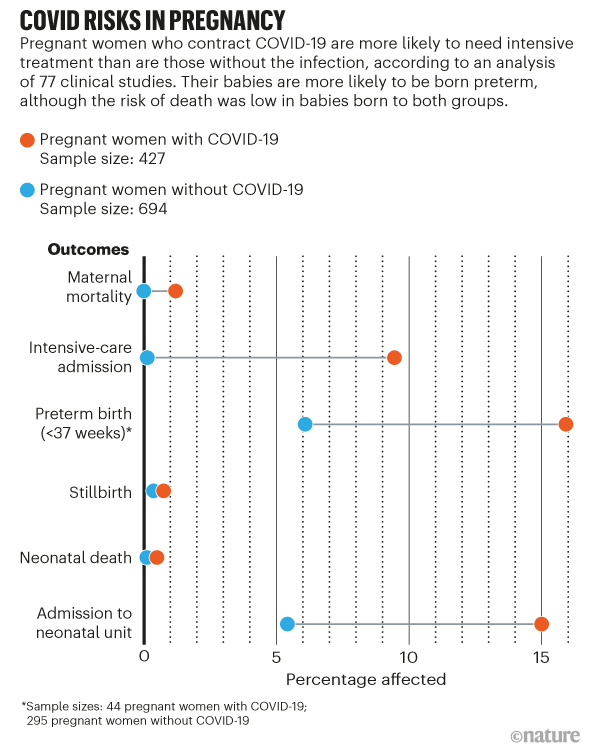
Pregnancy And Covid What The Data Say
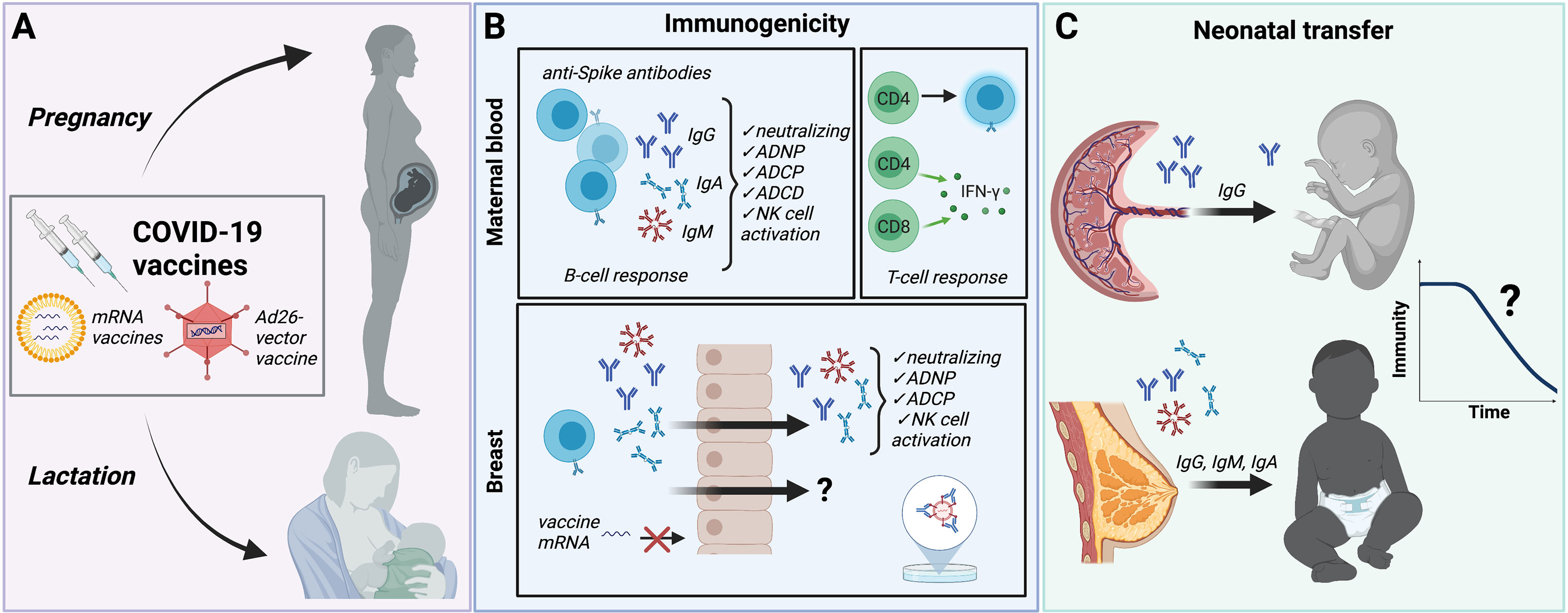
Frontiers Covid 19 Vaccination In Pregnancy And Lactation Current Research And Gaps In Understanding Cellular And Infection Microbiology